Today's Brief 7/12/2024
- Smriti IASxp

- Dec 7, 2024
- 3 min read
IE Analysis: https://youtu.be/cbKnmeUWGpE?feature=shared
JN Analysis: https://youtu.be/mfACUD1Dn1s?si=2OtrgEpIxa3noMBf
1 .France: is a republican State and a parliamentary democracy, often qualified as semi-presidential. The Parliament is bicameral and is made up of the National Assembly (Assemblée nationale) and the Senate (Sénat). The latter indirectly represents the sub-national authorities' interests to the extent that the Senate is indirectly elected by an electoral body comprising representatives of the Regions, the Departments and the Communes.
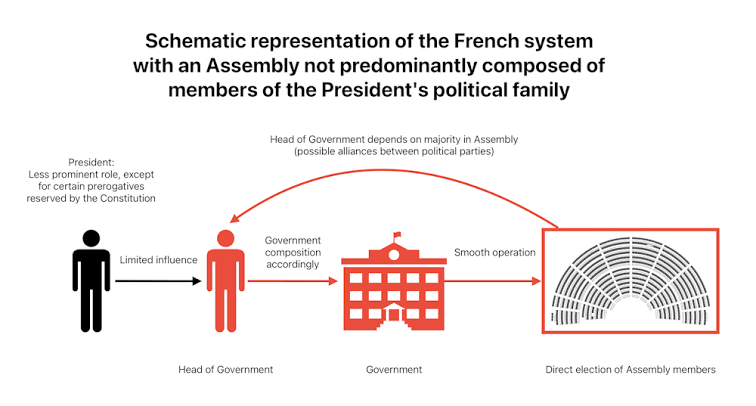
A “rationalised parliamentary regime" (parlementarisme rationalisé) was established by the 1958 Constitution, in favour of the Government.
However, a constitutional reform occurred in 2008 in order to rebalance the relationship between the Parliament and the Government, in favour of the former.
France is characterised by a flexible separation of powers, i.e. the Government is politically responsible before the Parliament but can, in turn, dissolve the National Assembly. operates under a semi-presidential system, combining elements of both presidential and parliamentary democracies.
President: Directly elected by popular vote, holds significant executive power, including appointing the Prime Minister.
Prime Minister: Heads the government and is responsible to the Parliament.
Parliament: Bicameral legislature consisting of the National Assembly (lower house) and the Senate (upper house).
Separation of Powers: Executive, legislative, and judicial branches function independently.
Unique Aspects:
Cohabitation: When the President and Prime Minister come from different political parties, leading to a power-sharing arrangement.
Strong Presidency: The President holds substantial authority, including the power to dissolve the National Assembly.
Referendums: The President can initiate referendums to directly consult the public on specific issues.
2 .PRAGATI (Pro-Active Governance and Timely Implementation): Since its launch in 2015, PRAGATI has emerged as a powerful tool for transforming India’s infrastructure landscape. By June 2023, the platform had reviewed 340 projects valued at ₹17.05 lakh crore ($205 billion), significantly expediting their implementation. This includes the development of 50,000 kilometres of National Highways and doubling the country’s airports, reflecting a decade of unparalleled progress.

The selection of these 340 projects was highly strategic, focusing on initiatives of national importance that presented unique and complex challenges. PRAGATI has been instrumental in addressing these 'wicked' projects, often considered the most daunting in terms of execution.
3 .Why low-intensity Cyclone Fengal caused large-scale destruction: While Cyclone Fengal was a low-intensity storm, its slow movement and prolonged presence over the affected regions led to widespread destruction.
Slow Movement and Stagnation:
Reduced Dissipation: Unlike fast-moving cyclones that dissipate quickly after landfall, Fengal's slow movement allowed it to maintain its intensity for a longer period.
Prolonged Rainfall: The slow pace resulted in continuous heavy rainfall over several hours, leading to flooding in low-lying areas.
Increased Wind Exposure: The stationary nature of the cyclone exposed regions to strong winds for an extended duration, causing significant damage to infrastructure and vegetation.
Heavy Rainfall:
Flooding: The torrential rainfall overwhelmed drainage systems, leading to widespread flooding in urban and rural areas.
Landslides: In hilly regions, heavy rainfall triggered landslides, causing further damage and loss of life.

Coastal Erosion:
Strong Winds and Waves: The strong winds and high waves eroded coastal areas, damaging infrastructure and causing coastal erosion.
Lack of Preparedness:
Underestimation of Impact: Despite being a low-intensity cyclone, its potential for widespread destruction was underestimated, leading to inadequate preparedness measures.
Delayed Response: The slow-onset nature of the disaster hampered timely response and relief efforts.



Comments