Today's Brief 14/08/2024
- Smriti IASxp

- Aug 14, 2024
- 8 min read
Updated: Aug 15, 2024
Youtube English:https://youtu.be/eswdLyTSlqQ?si=zy6cv9WRJI61P32L
Youtube Hindi: https://youtu.be/Dv6WNQ-nxC8?si=B01BlN0lFM2V3Fpy
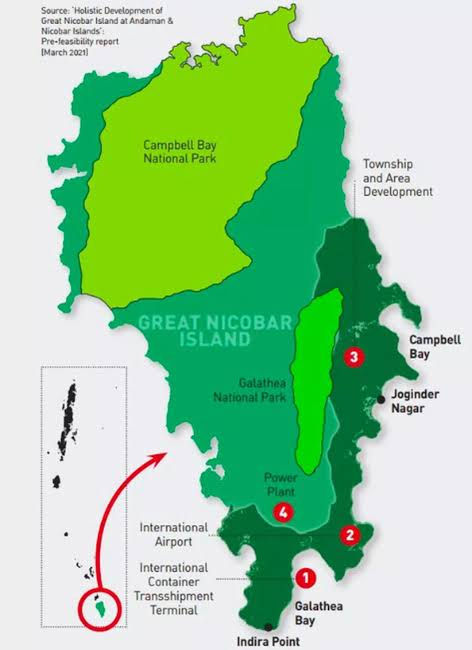
Great Nicobar Island: It is an ambitious project launched by the NDA government in 2021. The project was implemented after a report by NITI Aayog which identified the potential to utilize the advantageous position of the island.
The project is aimed at creating an International Container Trans-shipment Terminal(ICTT) on Great Nicobar Island. It also includes a Green Felid International Airport along with a Township. It is expected to be powered by the 450 MVA gas and solar-based power plant included in the project.
The ICTT and power plant are planned for Galathea Bay, in the southeastern corner of Great Nicobar Island, an area with no human habitation.
The location was chosen for its proximity to Malacca Strait. It is also approximately equidistant from Colombo (Sri Lanka), Port Klang (Malaysia), and Singapore, offering strategic advantages.
The Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways had projected that the Rs 41,000 crore (approximately USD 5 billion) port would be developed through a mix of government funding and public-private partnerships (PPP). Eleven companies, including Larsen and Toubro Ltd, Afcons Infrastructure Ltd, and JSW Infrastructure Ltd, have expressed interest in the project.
Great Nicobar Island is the southernmost and largest of the Nicobar Islands, located in the eastern Indian Ocean. It is part of the Indian Union Territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Here are some key details about Great Nicobar Island:
Geography and Location:
Location: It lies close to the northern tip of Sumatra, Indonesia, and is part of the Bay of Bengal.
Size: The island covers an area of approximately 1,045 square kilometers.
Topography: The island has a rugged terrain with dense tropical forests, rivers, and hills. The highest point on the island is Mount Thullier, which rises to about 642 meters.
Population:
The island is sparsely populated. The indigenous tribes, such as the Nicobarese and Shompen, are among the inhabitants. However, the majority of the island remains largely undeveloped and covered in rainforest.
Biodiversity:
Great Nicobar is rich in biodiversity and is home to the Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve, which is recognized by UNESCO. The reserve protects a range of flora and fauna, some of which are endemic to the island.
The island is also known for the Nicobar Megapode, a unique bird species that incubates its eggs in the sand.
Strategic Importance:
Given its location at the juncture of the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea, Great Nicobar Island holds significant strategic importance for India, particularly in terms of maritime security.
India has plans to develop infrastructure on the island, including a transshipment port and other military installations, as part of broader strategic initiatives in the region.
Recent Developments:
There have been plans and proposals for the development of Great Nicobar, including the creation of a new township and international transshipment port. These projects aim to boost the economic and strategic significance of the island, though they have also raised environmental and ecological concerns.
Connectivity:
The island is connected to mainland India by air and sea, although it remains relatively remote. The nearest major urban center is Port Blair, the capital of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, located about 540 kilometers to the north.
2. DDOS Attack: A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack is a type of cyberattack where multiple compromised systems (often infected with malware) are used to target a single system, such as a server, website, or network, causing a denial of service for users of the targeted resource. Here’s a breakdown of how DDoS attacks work and their implications:
How DDoS Attacks Work:
Infection: Attackers first compromise a large number of devices (these could be computers, IoT devices, etc.) by infecting them with malware. These compromised devices, collectively known as a "botnet," are controlled by the attacker.
Launch: The attacker instructs the botnet to flood the target with a massive amount of traffic. This traffic can take various forms, such as sending large numbers of requests to a web server or overwhelming network bandwidth with excessive data.
Overload: The target system becomes overwhelmed by the sheer volume of traffic, leading to service disruptions or complete outages. Legitimate users are unable to access the service or network because
the target cannot handle the excess load.
Types of DDoS Attacks:
Volumetric Attacks: These involve overwhelming the target's bandwidth with massive amounts of data. Examples include UDP floods and ICMP floods.
Protocol Attacks: These target weaknesses in the network protocol stack, such as SYN floods, which exploit the TCP handshake process.
Application Layer Attacks: These target specific applications or services, such as HTTP floods that overwhelm a web server with requests.
Impact of DDoS Attacks:
Service Disruption: The most immediate impact is the disruption of services, making websites or online services unavailable to legitimate users.
Financial Losses: Businesses can lose revenue due to downtime, and may also incur costs related to mitigating the attack and restoring services.
Reputation Damage: Persistent or successful attacks can harm the reputation of a business or organization, leading to a loss of customer trust.
Collateral Damage: Other systems or networks connected to the target may also experience performance issues due to the widespread nature of the attack.
Mitigation Strategies:
Firewalls and Routers: Configuring these devices to block malicious traffic can help mitigate some DDoS attacks.
Load Balancers: Distributing traffic across multiple servers can help absorb the impact of an attack.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs can cache content and distribute it across multiple locations, reducing the load on the target server.
DDoS Mitigation Services: Specialized services can detect and filter out malicious traffic before it reaches the target.
Recent Trends:
Increased Frequency and Sophistication: DDoS attacks have become more frequent and sophisticated, with attackers using new methods and targeting critical infrastructure.
Use of IoT Devices: The rise of IoT devices, many of which have weak security, has led to the creation of massive botnets that can be used in DDoS attacks.
3.Tarang Shakti exercise: The Indian Air Force is hosting its largest ever multilateral air combat exercise Ex Tarang Shakti at Sulur airbase of Indian Air Force in Tamil Nadu. It is aimed at showcasing its military capabilities and strengthening international cooperation.
This strategically significant exercise drawn participation from around 11 countries featuring a diverse array of aircrafts including Rafales, F-18, and Eurofighter. Ex Tarang Shakti exercise is designed to enhance India’s defence ties with the participating nations while demonstrating its Indigenous defence capabilities.
nternational Defence Aviation Exposition 2024 – IDAX 2024 is also being organised at Air Force Station at Sulur in Tamil Nadu.
4.MoSPI’s ‘women and men in India 2023’ reveals progress and gaps in gender equality: The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has released the 25th edition of its comprehensive publication, “Women and Men in India 2023.” This report offers a detailed look at the status of women and men across various sectors in India, providing crucial insights for policymakers and researchers.
The publication provides data on a wide range of topics such as Population, Education, Health, Participation in Economy, Participation in Decision making etc. among others.
It presents data disaggregated by gender, urban-rural divide, and geographical region, which helps to understand the disparities that exist between different groups of women and men.
publication includes important indicators as derived from published official data of different ministries, departments, and organizations.
“Women and Men in India 2023” not only highlights the progress made towards gender equality but also identifies the areas where significant gaps remain.
By 2036, India’s population is projected to reach 152.2 crore, with women comprising 48.8% of the total, up from 48.5% in 2011. The sex ratio is expected to improve from 943 in 2011 to 952 by 2036, indicating a more balanced gender distribution.
Age-specific fertility rates for women aged 20-29 have decreased between 2016 and 2020, while rates for women 35-39 have slightly increased. The report also highlights the significant impact of education on fertility rates, with literate women having much lower adolescent fertility rates compared to illiterate women.
5.National Space Day: The Government of India has declared August 23rd as "National Space Day" to celebrate the remarkable success of the Chandrayaan-3 Mission, which accomplished safe and soft landing of the Vikram Lander and deployed the Pragyaan rover on the lunar surface near the South Pole.
This historic achievement places India among an elite group of space faring nations, making India the fourth country to land on the Moon and the first to do so near the south pole of the Moon. This achievement is being celebrated across the country during July and August 2024, with the goal of engaging and inspiring the younger generation in the field of Space Science and Technology.
Chandrayaan-3 mission accomplished safe and soft-landing of Vikram Lander on the lunar surface on August 23, 2023. With this, India became the fourth country to land on the moon and first to land near the southern polar region of the moon.
The soft-landing was followed by successful deployment of Pragyan Rover. The landing site was named as 'Shiv Shakti' point (Statio Shiv Shakti) and August 23 was declared as the "National Space Day". India will celebrate its maiden National Space Day on August 23, 2024.

6.India added 3 Ramsar sites to the network, taking the tally to 85 Ramsar sites: Environment, Forest and Climate Change Minister Bhupendra Yadav today shared that India has added three Ramsar sites to the network, taking the tally to 85 Ramsar sites. Nanjarayan Bird Sanctuary and Kazhuveli Bird Sanctuary in Tamil Nadu and Tawa Reservoir of Madhya Pradesh have been added to the list of India’s Ramsar sites.
The Ramsar Convention, formally known as the Convention on Wetlands of International Importance especially as Waterfowl Habitat, is an international treaty focused on the conservation and sustainable use of wetlands. Here’s a detailed overview:
Overview:
Adoption: The Ramsar Convention was adopted on February 2, 1971, in the city of Ramsar, Iran, hence the name. It came into force in 1975.
Purpose: The primary objective of the Ramsar Convention is to promote the conservation and wise use of wetlands through local, regional, and national actions and international cooperation. It recognizes the ecological functions of wetlands as well as their economic, cultural, scientific, and recreational value.
Key Features:
Wetlands of International Importance (Ramsar Sites):
The Convention provides a framework for the designation of wetlands of international importance. These sites are selected based on their ecological, botanical, zoological, limnological, or hydrological significance.
Each country that joins the Convention, known as a "Contracting Party," is required to designate at least one wetland site for inclusion in the Ramsar List of Wetlands of International Importance.
As of now, there are over 2,400 Ramsar sites worldwide, covering more than 250 million hectares.
Wise Use Concept:
The concept of "wise use" is central to the Ramsar Convention. It refers to the maintenance of the ecological character of wetlands through the implementation of ecosystem approaches, within the context of sustainable development.
The idea is to balance the conservation needs of wetlands with the needs of local communities and economic development.
International Cooperation:
The Convention encourages international cooperation, especially for shared wetlands and water systems, and migratory species of waterfowl.
It also emphasizes the importance of cross-border collaboration in managing shared wetland resources.
Monitoring and Reporting:
Contracting Parties are required to report on the condition of their Ramsar sites and the measures they are taking to maintain their ecological character.
Regular Conferences of the Contracting Parties (COP) are held to review the implementation of the Convention and discuss new issues and priorities.
Importance of Wetlands:
Wetlands are critical ecosystems that provide a range of services, including water purification, flood control, carbon storage, and habitat for biodiversity, especially migratory birds.
They are also important for human well-being, providing resources such as food, fresh water, and raw materials, and supporting livelihoods, especially in rural areas.
World Wetlands Day:
February 2, the anniversary of the adoption of the Convention, is celebrated annually as World Wetlands Day to raise awareness about the importance of wetlands.
India's Role:
India is a signatory to the Ramsar Convention and has designated numerous Ramsar sites across the country. Some of the prominent ones include Keoladeo National Park, Chilika Lake, and Sundarbans Wetland.
Refrence:
PIB, Indian Express, The Hindu



Comments